Fractions
Terms
Numerator: which tells how many parts you
have (the number on top)
Denominator: which tells how many parts in
the whole (the number on the bottom)
Example:
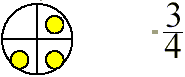 is 3 parts have a dot out of 4
is 3 parts have a dot out of 4
Proper fraction: the top number is less than
the bottom number.
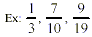
Improper fraction: the top number is equal to
or is larger than the bottom number.
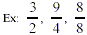
Mixed Number: a whole number is written next
to a proper fraction.
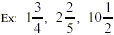
Common Denominator: is a number that can be
divided evenly by all of the denominators in the problem
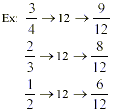 The common denominator for these fractions will be 12. It also
happens to be least common denominator.
The common denominator for these fractions will be 12. It also
happens to be least common denominator.
Reducing Fractions to Lowest Terms
Example:
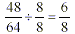
Step 1: Find a number that goes evenly into
the numerator and the denominator of the fraction. With the
fraction to the left, the number that will go in evenly is 8.
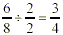
Step 2: Check to see whether another number
goes evenly into both the numerator and denominator. Stop when
there are no more numbers that can go into the fraction.
In the example, the fraction can be reduced further by
dividing it by 2.
Changing Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
Example: Change 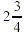 to an
improper fraction. to an
improper fraction.
2 × 4 = 8 Step 1: Multiply the denominator
by the whole number.
8 + 3 = 11 Step 2: Add the result to the
numerator.
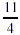 Step
3: Place the total over the denominator. Step
3: Place the total over the denominator.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Different Bottom
Numbers
Example 1:
Step 1: Need to find the common denominator
for all fractions.
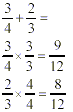
Step 2: Then go ahead and add or subtract the
fractions.
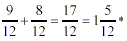
*Remember to change improper fractions to a mixed number.
Multiplying Fractions
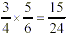 Multiply the numerators across. Then multiply the denominators
across. Make sure the product is in lowest terms.
Multiply the numerators across. Then multiply the denominators
across. Make sure the product is in lowest terms.
Multiplying with Mixed Numbers
Example
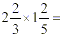
Step 1: Change every mixed fraction to an
improper fraction.
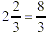
Step 2: The multiply across.
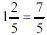
Step 3: Then, change the improper fraction to
a mixed number in lowest terms.

Dividing Fractions
Example: 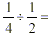
The fraction that is right of the division sign will need to
be turned upside down by writing the numerator in the denominator
and the denominator in the numerator. Then follow the rules for
multiplying fractions.
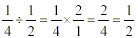
|