Multiplying Fractions
Many situations require us to multiply fractions. For
instance, suppose that a mixture in a chemistry class calls for 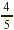 g of sodium chloride. If we make only g of sodium chloride. If we make only 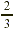 of that mixture, we need of that mixture, we need 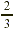 of of 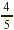 , that is, , that is, 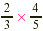 g of sodium chloride. g of sodium chloride.
To illustrate how to find this product, we diagram these two
fractions.
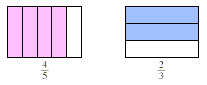
In the following diagram, we are taking 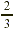 of the of the 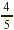 . .
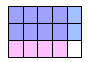
Note that we divided the whole into 15 parts and that our
product, containing 8 of the 15 small squares, represents the
double-shaded region. The answer is therefore 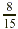 of the original whole, which we can compute as
follows. of the original whole, which we can compute as
follows.
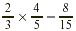
The numerator and denominator of the answer are the products
of the original numerators and denominators.
To Multiply Fractions
- first multiply the numerators,
- then multiply the denominators, and
- finally write the answer in simplest form.
EXAMPLE 1
Multiply: 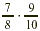 . .
Solution
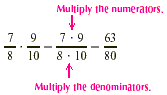
EXAMPLE 2
What is 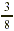 of 10? of 10?
Solution
Finding 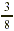 of 10 means multiplying of 10 means multiplying 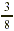 by 10. by 10.
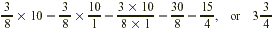
In Example 2, we multiplied the two fractions first and then
simplified the answer. It is preferable, however, to reverse
these steps: Simplify first and then multiply. By first
simplifying, which is called canceling, we divide any numerator
and any denominator by a common factor. Canceling before
multiplying allows us to work with smaller numbers and still
gives us the same answer.
EXAMPLE 3
Find the product of 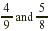 . .
Solution
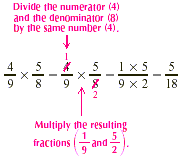
EXAMPLE 4
Multiply: 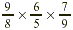 . .
Solution
We cancel and then multiply.
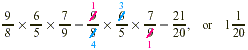
EXAMPLE 5
At a college, 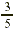 of the students take a math course. Of these
students, of the students take a math course. Of these
students, 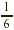 take elementary algebra. What fraction of
the students in the college take elementary algebra? take elementary algebra. What fraction of
the students in the college take elementary algebra?
Solution
We must find 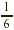 of of 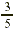 . .
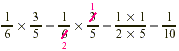
One-tenth of the students in the college take elementary
algebra.
EXAMPLE 6
Suppose that you spend 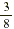 of your monthly salary on rent. If your salary is
$960, how much do you have left after paying the rent? of your monthly salary on rent. If your salary is
$960, how much do you have left after paying the rent?
Solution
Apply the strategy of breaking the question into two parts.
- First, find
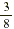 of $960. of $960.
- Then, subtract that result from $960.
Thus you can solve this problem by computing 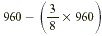 . .
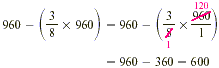
You have $600 left after paying the rent.
|